Building Service : Telephone
DEFINITION
The mean of telecommunication is the transmission of messages, over significant distances for the purpose of communication.
The mean of telephone is describes the long distance transmission of information without changing the content of such information. A telephone is any device which conveys sound over a distance. A standard dictionary defines the telephone as ‘an apparatus for reproducing sound, especially that of the voice, at a great distance, by means of electricity; consisting of transmitting and receiving instruments connected by a line or wire which conveys the electric current.’
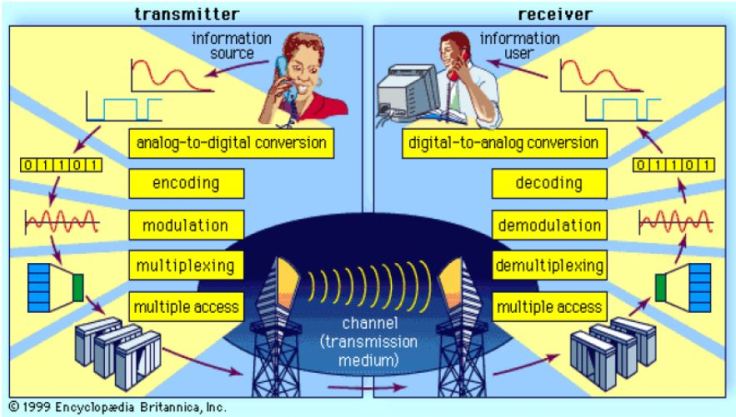
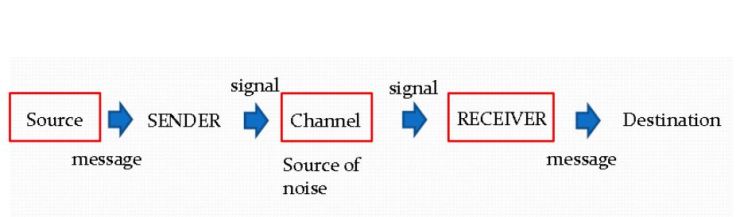
The components of telecommunication system
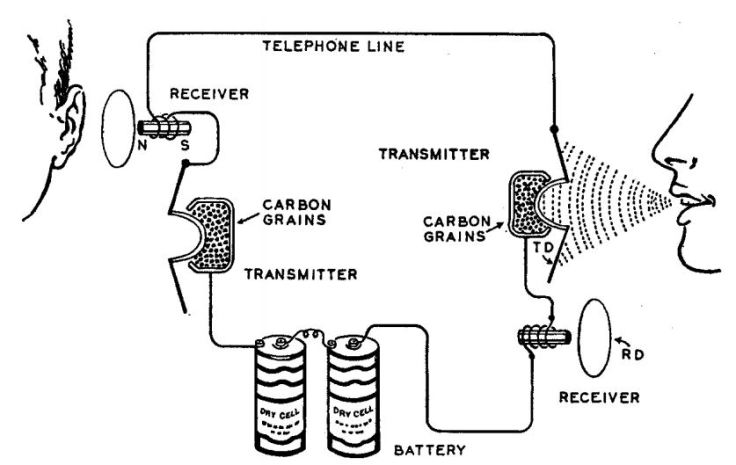
- Sender / Transmitter
The sender or transmitter used for creating information and takes information ; converts it to a signal
- Channel / Transmission medium
The channel or transmission medium used for carries the signal and information will be sent through it.
- Receiver
The receiver used for takes the signal from the channel and converts it back into usable information.. That also receives information transmitted without any changes.
The difference between analog and digital communication
| Analog communication | Digital Communication |
| 1.Continuous waveform | Discrete waveform |
| 2.Voice signal is transmitted over conventional telephone system as variation in the line voltage along copper cables. | 2.A signal can be represented by a series of 1 and 0 and transmitted |
| 3.Used for voice communication | 3Used for data communication |
How the telecommunication system work?
A main distribution frame is a signal distribution frame or cable rack used in telephony to interconnect and manage telecommunication wiring between itself and any number of intermediate distribution frames and cabling from the telephony network it support.
For domestic building overhead cable entry is usually provided. For larger commercial building the cable connection from outside enters the building from underground. For single domestic building the telephone cable is in form of a twisted pair. For larger building with many telephone extension, a room adjacent to the MDF room is provided to house the private automatic branch exchange equipment.
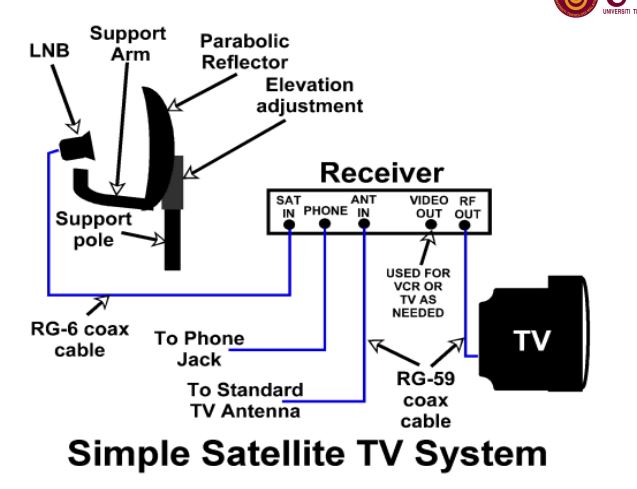
Cable television (CATV) is a system of delivering telkevision programming to paying subscribers via radio frequency signals transmitted through coaxial cable or in the 2010, light pulses through fiber optic cable.
CATV(Community Access Television)
It originally stood for Community Access Television or Community Antenna Television, from cable television’s origins in 1948. In areas where over-the-air TV reception was limited by distance from transmitters or mountainous terrain, large “community
antennas” were constructed, and cable was run from them to individual homes.
Cable television is a system of delivering television programming to paying
subscribers via radio frequency (RF) signals transmitted through coaxial cables or, in the
2010s, light pulses through fiber-optic cables. This contrasts with broadcast television, in
which the television signal is transmitted over the air by radio waves and received by
a television antenna attached to the tv.
A cable channel/network is a television network available via cable television. When
available through satellite television, including direct broadcast satellite providers
such as ASTRO as well as via IPTV, it is referred to as a satellite channel.