Electrical and Lighting System
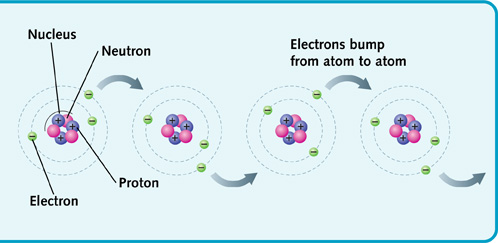
In aspect atomic theory of principles electricity, everything in the universe is made up of matter that exist as liquid, solid or gas. Matter can be broken down into small particles that called atoms. An atom is made up of protons (positive charge), neutrons (negative charge) and electrons (no charge). Protons and neutrons are gathered together in the center of the atom. While, electrons spin around the nucleus in an orbit. Have three condition such as neutral charge if an atom has the same number of electrons and protons, negatively charge if an atom has more electrons than proton and positively charge if an atom has less electrons than proton.
In aspect flow of principles electricity, get two type flow such as current flow (current was assumed to flow through a conductor from positive to negative (+>>-). While, electron flow (electrons flow from the negative terminal of a power supply towards the positive terminal of the power supply through an electrical circuit (->>+).
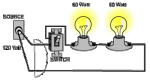
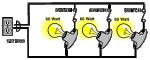
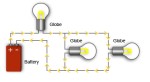
In aspect circuit of principles electricity, have three type circuit such as series (one path only), parallel (more than one path) and combination (both of series and parallel).
| Series Circuit | Parallel Circuit | Combination Circuit |
| -Has two or more loads connected, one after the other
-Is the single current path, no any branches |
-Removing or adding loads to a parallel circuit does not affect any other load in the circuit.
-Has more than one path |
-Is a combination of the series and parallel circuits
-Some section of the circuit are series and other are parallel. |
In aspect Ohm’s law, voltage, current and resistance are present in all operational circuits and a relationship exists between these things which current flow in a circuit is directly proportional to the voltage across the circuit and inversely proportional to the resistance contained in the circuit.
Formula Ohm’s can be defined as below
V = IR
Voltage = current x resistance
In aspect of source of power generation, there are six sources of electromotive force such as chemical, light, magnetism, pressure and heat.
| Chemical | -A battery uses a chemical effect to produce electromotive force.
-The chemical effect is achieved by placing two dissimilar metals into an electrolyte. -When a battery cell is connected to an external source, its chemical energy will decrease as the cell produces electrical energy. -When the chemical energy of a dry cell battery has expired it will no longer deliver electrical energy. -This make it a temporary voltage source. |
| Light | -The sun rays can be used to produce a voltage potential.
-This is achieved using a solar cell (commonly called a photoelectric). -The solar cell is a thin junction made of two different types of semiconductor materials. -Light falling onto these semiconductors causes electrons to move freely. -The most common types of semiconductor used are silicon, boron and phosphorus. |
| Magnetism | -The most common way of creating an electromotive force is by using magnetism.
-When a conductor passes through a magnetic field, cutting through a voltage is induced into the conductor. -Used in wind generators, tidal generation and hydro plants to creating electromotive force. |
| Heat | -The heat effect is the direct conversion of temperature differences to electric voltage and vice versa.
-A heat device creates voltage when there is a different temperature on each side. -Conversely, when a voltage is applied to it, it creates a temperature difference. |
| Pressure | -The pressure from an electrical circuit’s power source that pushes charged electrons (current) through a conducting loop, enabling them to do work such as illuminating light. |
In aspect sequence control circuit, that mean as the sequence of control and protective devices contain in the main circuit and consumer final circuit. The sequence control circuit divided into supply part and consumer part. The supply part include service fuse and neutral link that known as protection against excessive current and limiting consumer current and KWH meter that used for recording power usage and charge. While, the consumer part include interface between utility company and consumer wiring and consist three main devices such as main switch, Residual current circuit breaker and miniature circuit breaker.

Leave a comment