NATURAL GAS
DEFINITION OF GAS
The word ‘gas’ is defined under Act 501 as “methane, propane, butane or hydrocarbon or containing one or more of the above either in gas or liquid form’.
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (another is solid, liquid and plasma.
A pure gas is made up of individual atoms (neon), elemental molecules (oxygen) or compound molecules (carbon dioxide).
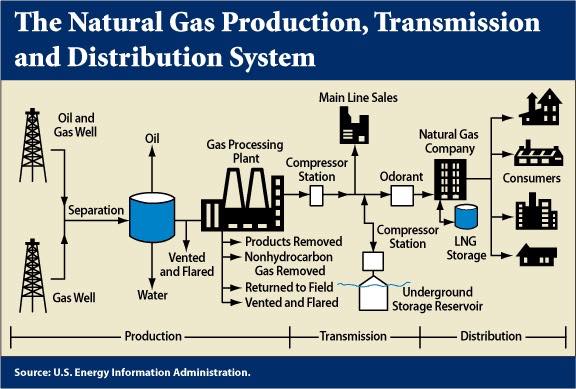
The gas will be channeled to the Gas Separation Unit in which carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide in the gas are remove to avoid freezing and clogging from happening in the Liquidation Unit.
Next, the gas is channel to the drying unit in which bubbles of steam will be removed. Subsequently, the gas will be delivered to Fragmentation Unit to be broken down into various components such as ethane and propane are used as refrigerant, while benzene paraffin will be removed to avoid freezing and clogging occurs during the liquidation process.
The remaining gas will be delivered to the Liquidation Unit where it will be liquefied by cooling it to a temperature of –161’C by using coolant.
DEFINITION OF NATURAL GAS
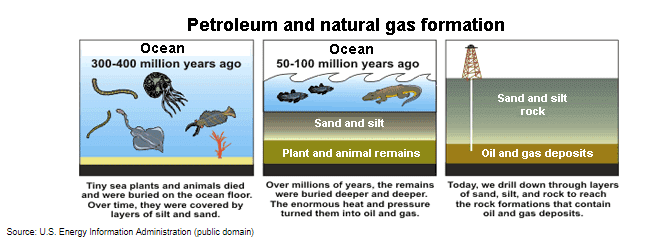
- Natural gas occurs deep beneath the earth’s surface.
- Natural gas consists mainly of methane, a compound with one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms.
- Natural gas also contains small amounts of hydrocarbon gas liquidsand non-hydrocarbon gases.
- We use natural gas as a fuel and to make materials and chemicals.
USERS
- Residential
Require energy on a constant basis to heat our water, cook our food, warm our homes, and generate our electricity. The most common use for natural gas around the home is for furnaces and hot water tanks. Natural gas can also be used to operate various household appliances, including stoves, clothes dryers, fireplaces, and barbecues.
- Commercial
Schools, office buildings, hotels, restaurants and many other commercial enterprises use natural gas. As with residences, these enterprises use the gas mainly for heating, cooling, and cooking. Large commercial enterprises are also beginning to use natural gas for on-site electricity generation as an economical alternative to purchasing electricity off-site.
- Industrial
Natural gas has numerous uses in the petroleum refining, metal, chemical, plastic, food processing, glass and paper industries. The ingredients for plastic, anti-freeze, fertilizer, and fabric products are formed through the use of natural gas by-products. The fact that natural gas is one of the cleanest, cheapest, and most efficient sources of energy makes it easy to see why it is so commonly used.
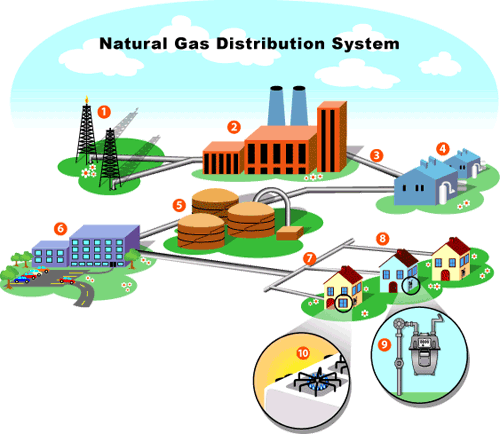
TRANSPORTATION
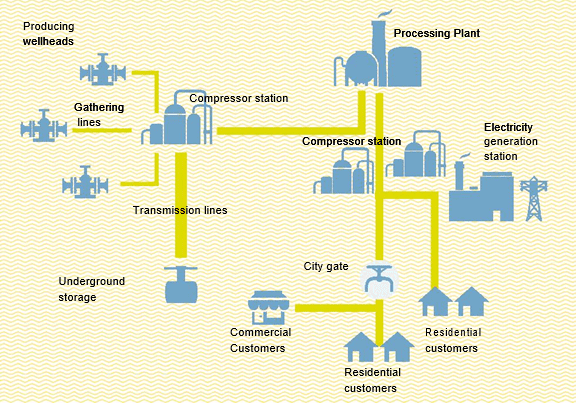
- Transmission pipelines.
- A transmission pipeline transports the natural gas from the Gas Processing Plant (GPP) to the distribution center and to larger volume customers.
- This transmission pipeline ends at the city gate station and transports the natural gas within the storage field.
- Distribution pipelines.
- A distribution pipeline supplies and distributes the natural gas from the city gate station to the end-users.
- Normally, the pressure of the natural gas would be reduced and the gas is odorized for safety purpose at the city gate station.
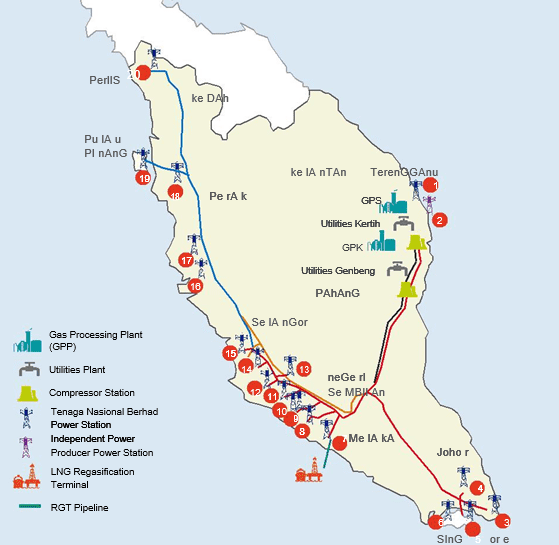
PENINSULA GAS UTILIZATION (PGU)
- Approximately 2583 km of high pressure natural gas transmission pipeline in the Peninsular Malaysia is solely managed by PETRONAS Gas Berhad (PGB).
- This natural gas transmission pipeline, known as Peninsular Gas Utilisation (PGU), serves as the backbone of Peninsular Malaysia’ natural gas supply infrastructure.
- The pipelines are operated and maintained by PETRONAS Gas Berhad (PGB).
- Technically, the natural gas utilized in the National Gas Power Generation is supplied by the PGB through the PGU system which is connected to the Power Generation facilities.
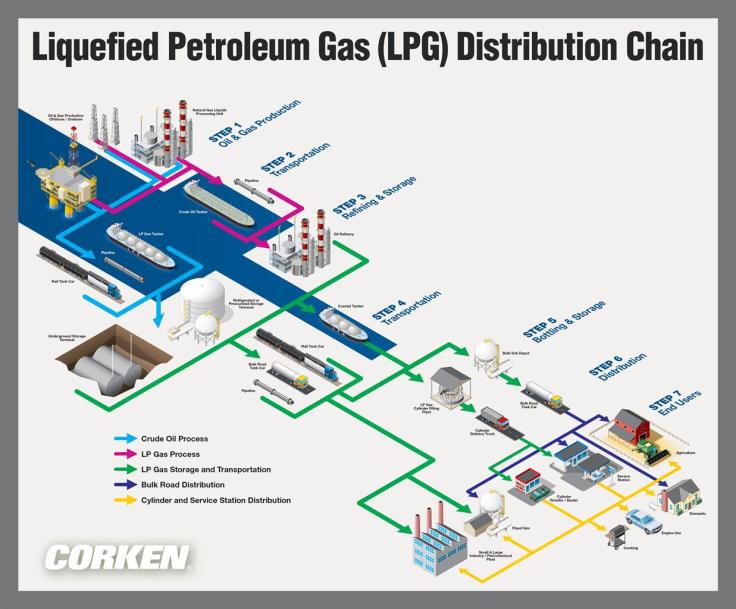
LIQUID PETROLEUM GAS (LPG)
- LPG (Liquid Petroleum Gas) describes flammable hydrocarbon gases including propane, butane and mixtures of these gases.
- LPG, liquefied through pressurisation, comes from natural gas processing and oil refining.
- LPG is used as heating, cooking and auto fuel.
- In different countries, what is supplied can be propane, butane or propane-butane blends.
GAS PIPING SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
NATURAL GAS DISTRIBUTION
- Local distribution companies typically transport natural gas from delivery points located on interstate and intrastate pipelines to households and businesses through thousands of miles of small-diameter distribution pipe.
- The delivery point where the natural gas is transferred from a transmission pipeline to the local gas utility is often termed the ‘citygate’, and is an important market center for the pricing of natural gas in large urban areas.
LPG PIPING SYSTEM

Leave a comment